Full Text:
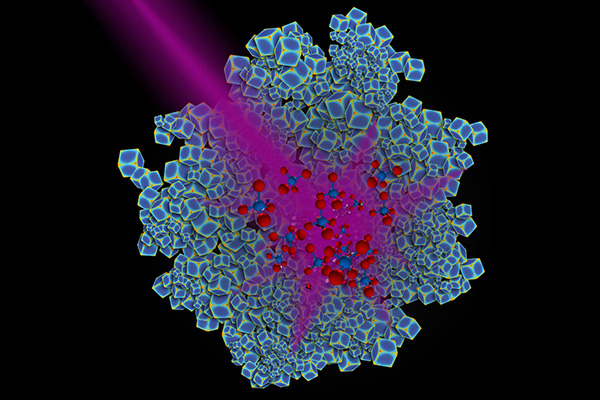
Duke University researchers have engineered rhodium nanoparticles (blue) that can harness the energy in ultraviolet light and use it to catalyze the conversion of carbon dioxide to methane, a key building block for many types of fuels. Having found a catalyst that can do this important chemistry using ultraviolet light, the team now hopes to develop a version that would run on natural sunlight, a potential boon to alternative energy.
Chemists have long sought an efficient, light-driven catalyst to power this reaction, which could help reduce the growing levels of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere by converting it into methane, a key building block for many types of fuels.Image credit: Chad Scales