Full Text:
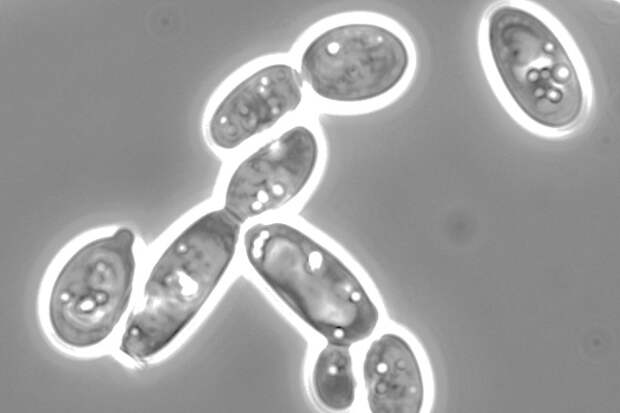
A team led by a researcher at the University of California, Riverside, has adapted the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing system for use in a yeast strain that can produce useful lipids and polymers. The development will lead to new precursors for biofuels, specialty polymers, adhesives and fragrances.
The research involves the oleaginous (oil-producing) yeast Yarrowia lipolytica, which is known for converting sugars to lipids and hydrocarbons that are difficult to make synthetically. Until now, Y. lipolytica has been hard to manipulate at the genetic level, but the application of CRISPR-Cas9 will change that, allowing scientists to tap into its bio-manufacturing potential.Image credit: Cory Schwartz, Chemical and Environmental Engineering, UC Riverside
